Reading through some bolt charts for Hex and Allen I came across some information that I figured I would share with the group. I also attached the link to the Fastenel technical data sheet if you ever have any questions.
By Default all Chrome Allen Head bolts should be classified at minimium of grade 8
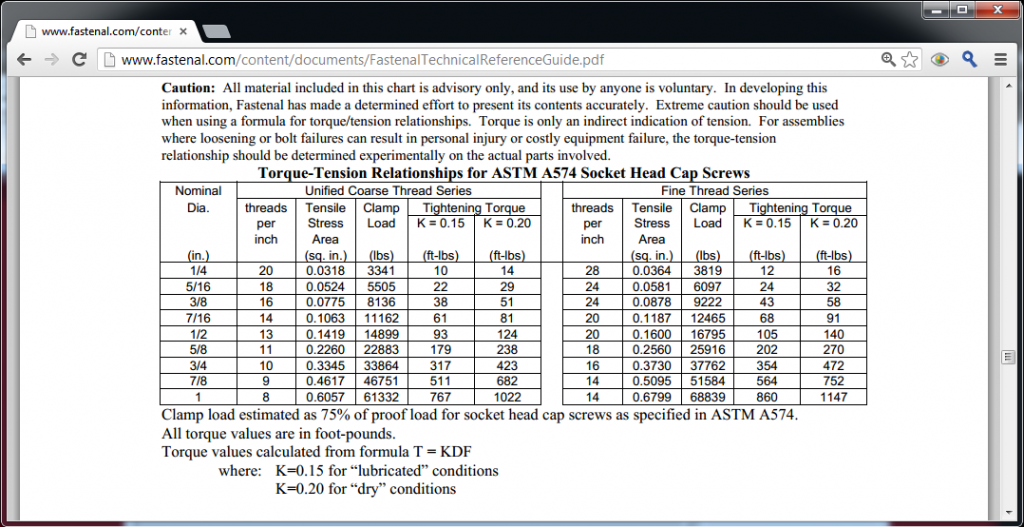
As we mainly use allen head bolts in most of our applications look for the markings "A574" on them and those are stronger than grade 8 with a minimium of Tensile Strength: 180,000 PSI minimum (through ½”), 170,000 PSI minimum (above ½”). :up:
http://www.fastenal.com/content/documents/FastenalTechnicalReferenceGuide.pdf
By Default all Chrome Allen Head bolts should be classified at minimium of grade 8
As we mainly use allen head bolts in most of our applications look for the markings "A574" on them and those are stronger than grade 8 with a minimium of Tensile Strength: 180,000 PSI minimum (through ½”), 170,000 PSI minimum (above ½”). :up:
http://www.fastenal.com/content/documents/FastenalTechnicalReferenceGuide.pdf
The following example will demonstrate the effectiveness of tempering:
ASTM A193 Grade B7, SAE J429 Grade 8 and ASTM A574 Socket Head Cap Screws are all made from
alloy steels. In fact some alloy steel grades can be used to manufacture any of the three final products:
such as 4140 and 4142 alloy steel. The final mechanical properties are the following:
ASTM A193 B7
• Tensile Strength: 125,000 PSI minimum (2-1/2-inch and under)
• Yield Strength: 105,000 PSI minimum (2-1/2-inch and under)
• Hardness: HRC 35 Maximum
SAE J429 Grade 8
• Tensile Strength: 150,000 PSI minimum 9
• Proof Strength: 120,000 PSI
• Yield Strength: 130,000 PSI minimum
• Hardness: HRC 33-39
ASTM A574 Socket Head Cap Screw
• Tensile Strength: 180,000 PSI minimum (through ½”), 170,000 PSI minimum (above ½”)
• Proof Strength: 140,000 PSI (through ½”), 135,000 PSI (above ½”)
• Yield Strength: 153,000 PSI minimum
• Hardness: HRC 39-45 (through ½”), HRC 37-45 (above ½”)
The initial heat-treating process is relatively the same for all three products. The parts are heat treated until
fully austenitized. The parts are then quenched and tempered in a liquid (oil). This final tempering
temperature is what will dictate our final product. The following are the minimum tempering temperatures
for each specification:
• ASTM A193 B7: 1150°F
• SAE J429 Grade 8: 800°F
• ASTM A574: 650°F



